By Dr Than Lwin Tun
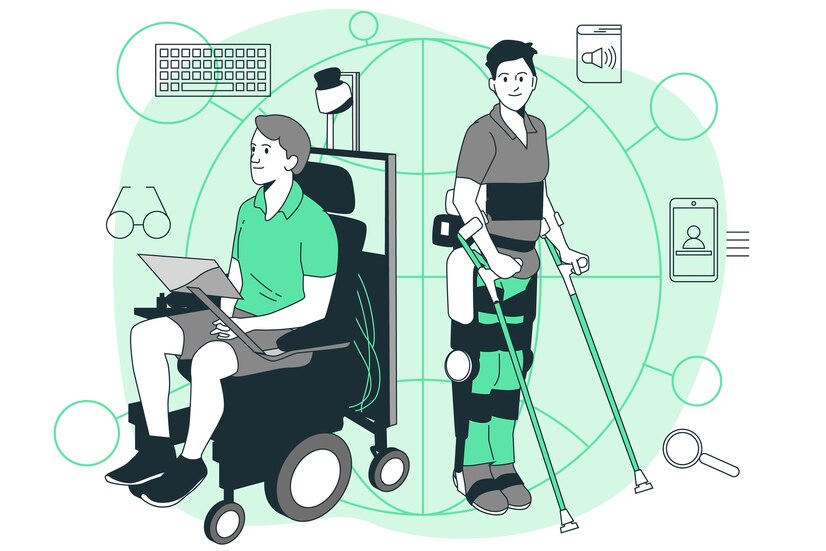
Assistive technology refers to any tools, devices, software, or equipment designed to assist people with disabilities in performing tasks that might be otherwise challenging or impossible for them. It enables and promotes inclusion and participation, especially of persons with disabilities, ageing populations, and people with non-communicable diseases. They enable people to live healthy, productive, independent and dignified lives and to participate in education, the labour market and civil life. The primary goal of medical assistive technology is to enhance the quality of life, independence, and inclusion of individuals with disabilities by providing them with the means to interact with the world around them more effectively.
There are various categories of assistive technology, each designed to address different types of disabilities and challenges.
- Mobility and Accessibility: Wheelchairs and Mobility Scooters: For people with mobility impairments, walking aids such as canes, crutches, and walkers to assist with balance and walking, ramps and lifts.
- Communication: augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices, tools that help individuals who have difficulty speaking communicate through symbols, pictures, or text-to-speech technology, and speech-to-text software that converts spoken words into written text, benefiting individuals with speech impairments.
- Visual Impairment: Screen readers, the software that converts on-screen text into synthesized speech or Braille output for individuals with visual impairments; Braille displays, devices that convert digital text into Braille characters for tactile reading.
- Hearing Impairment: Hearing aids, which amplify sound for individuals with hearing loss; closed captioning; and subtitles, which provide a text-based representation of audio content for people with hearing impairments.
- Cognitive Disabilities: cognitive assistive software, tools that help individuals with cognitive impairments manage tasks, schedules, and reminders; text-to-speech and speech-to-text tools that can aid individuals with reading or writing difficulties.
- Learning Disabilities: Educational software, the programs designed to support learning and comprehension for individuals with learning disabilities, text-to-speech and speech-to-text tools, which assist in reading and writing tasks.* Environmental Control: Smart home technology allows individuals with mobility impairments to control home appliances, lights, and more using voice commands or other accessible methods.
- Writing Helper: Tools that are designed to give detailed information on the self-written article, such as word counters.
- Prosthetics and Orthotics: artificial limbs (prosthetics) and supportive devices (orthotics) that help individuals regain mobility and function.
- Medical Devices: insulin pumps, medical alert systems, and other devices that help manage medical conditions.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that today 2.5 billion people need one or more assistive products, such as wheelchairs, hearing aids, or apps that support communication and cognition. With a global aging population and a rise in non-communicable diseases, this number will rise beyond 3.5 billion by 2050, with many older people needing two or more products as they age. While supporting independence and well-being, assistive products can help to prevent or reduce the effects of secondary health conditions, such as lower limb amputation in people with diabetes. They can also reduce the need for and impact on careers and mitigate the need for formal health and support services. Moreover, access to appropriate assistive products can have a tremendous impact on community development and economic growth.
Despite the global need for and recognized benefits of assistive products, access to assistive products remains limited. Addressing this unmet need is essential to progress towards the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals and realizing the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities. On March 28 and 29, 2023, the WHO Assistive Technology team hosted a meeting in Geneva to review the methodology, outcome and dissemination of the WHO Rapid Assistive Technology Assessment (rATA) survey and plan for further strengthening this important data collection tool.
The rATA is a population-based household survey that measures the self-reported need, demand, and barriers to accessing assistive technology. A global data collection effort from 2019 to 2021 saw the implementation of rATA in 35 countries and informed the WHO-UNICEF Global Report on Assistive Technology published in May 2022. The meeting brought together 28 stakeholders from 18 countries who were involved in the development, delivery, and analysis of rATA data. Participants discussed their experience and learning from rATA data collection and together identified priority actions to improve the questionnaire, increase efficiency in rATA implementation, better support country implementation, strengthen data management and analysis, and increase dissemination of rATA results.
Investing in effective and efficient assistive technology data collection is key to being able to inform evidence-based policies and programmes, measure progress in improving access to good-quality assistive products and services, and ultimately ensure equitable access to assistive technology for everyone in need. In addition, assistive technology plays a crucial role in enabling people with disabilities to participate more actively in education, employment, communication, and daily life. It continues to evolve with advancements in technology, making it increasingly personalized, user-friendly, and effective for addressing a wide range of disabilities and challenges.
References
– www.who.int/health-topics/assistive-technology
– www.who.int/news/item/30-03-2023-lessons-learnt-from-the-multi-country-rapid-assistive-technology-assessment-(rata)-survey